Computer Organization & Architecture
Itanium 2 Cache Organization
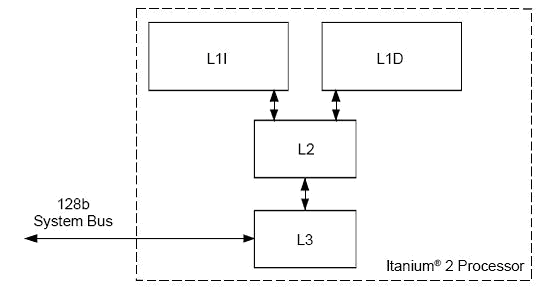
The Intel Itanium 2 employs three levels of on-chip non-blocking cache. It employs a 6 wide, 8 deep pipeline running at either 1.0GHz or 900MHz.
The level 1 cache is split into an instruction cache and a data cache. The level 1 instruction cache is fully pipelined and employs a prefetcher using branch prediction to avoid cache misses. It is dual ported, using one port for instruction fetches and the other port is shared for prefetches, snoops, fills and column invalidates. It can deliver 2 instruction bundles or 6 instructions per clock cycle. The cache is 16KB in size, single cycle and 4-way set associative with a line size of 64 bytes.
The level 1 data cache is quad ported, supports 2 concurrent loads and 2 stores. It is 16KB in size and is 4-way set associative having a line size of 64 bytes. It has a write-through with no write allocation policy. This cache only processes integer loads � integer stores and floating point loads and stores are processed by the level 2 cache. It has a cache read bandwidth of up to 64GB/s and has a write-back with write allocate policy.
The level 2 unified cache is an out of order cache, quad ported and can be accessed at full clock speed. Instructions are accessed using 4 ports and data can be accessed using 1, 2, 3 or 4 ports. 4 concurrent accesses are supported via banking. It is 256KB in size and is 8-way set associative with a line size of 128 bytes and is made up of 16 banks. The level 2 cache handles all floating point accesses and all semaphore instructions.
The level 3 unified cache is either 1.5MB or 3MB in size and can be accessed at core speed, providing 32GB/cycle. It is single ported and fully pipelined. The cache is 12-way set associative with a 128 byte line size. It supports 8 outstanding requests, 7 loads or stores and 1 fill. Both tag and data are protected using single bit correction and double bit detection. This means that any errors in the data that occur can be detected up to 2 bits out (reserving 5 bits to make this comparison) and will be corrected if it is 1 bit out.